what are the chances that the biopsy onmy right breast can be nothing due to menstuation
Complex Breast Cyst
A 'complex' or 'complicated' breast cyst, refers to cysts that contain something likewise clear fluid. A simple chest cyst, on the other manus, but contains articulate fluid. Indeed, this is commonly something harmless like an old blood clot or droppings

Simple cysts are supposed to have thin walls and contain only articulate fluid.
Complex breast cysts account for approximately five% of breast cysts that are nowadays on screening mammograms. And then, commonly a complex cyst of the breast indicates close follow-up and sometimes a biopsy.
There is a very very small adventure that a complex breast cyst could be associated with malignant breast cancer, then they merit a higher caste of scrutiny.
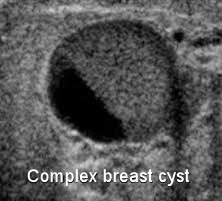

I look at this, and I know information technology'due south non cancer.
Ultrasound features of a Circuitous Cyst of the Breast
There are no standard definitions or signature features of a complex cyst. Indeed, these types of cysts are a heterogeneous (or varied) group of lesions with unlike presentations.
On ultrasound, radiographers will typically evaluate a complex breast cyst in terms of the post-obit features:-
- Internal echoes
- The presence or absence of posterior enhancement (evidence of an intracystic mass)
- Sparse septations
- A thickened and/or irregular wall (lobulations).
And then, the results of the ultrasound can influence the strategy for follow-up evaluation or treatment.
The radiologist will be looking for…
Findings of septations (thin walls that divide the cysts into segments) are really of little business organization. What the radiologist is looking for is hard bear witness of an intracystic mass, which would be indicative of neoplastic cell growth, and that would probably lead to histological evaluation. Even so, the chances of the neoplasm being chest cancer are very low.

If a breast cyst contains a septation, it'south not a cancer. Cancers grow into round shapes, not slender dividing-walls between fluid.
The determination to biopsy a complex cyst remains subjective
Findings of internal echoes without a distinctly visible solid mass or, alternatively, an 'anechoic' lesion with no posterior-wall enhancement would be a flake of a sentence call.
It probable means that various particles are floating in the cystic fluid and, and the complex cyst is extremely likely to be completely benign. ( It could exist floating cholesterol crystals, claret, pus, or milk of calcium crystals.) The conclusion to biopsy, or aspirate, or simply follow upward with observation, would be somewhat subjective in this example.
Higher risk of malignant association when in that location are irregular lobule shapes in the margin
The presentation of complex cysts and actual malignancy development, when it rarely occurs, can be a trivial bit irrational. The presence of an intracystic mass (likely neoplasm) does non statistically correlate with a college risk of malignancy.
But a thick cystic wall, lobulation (irregular lobule shapes in the wall), and hyperechogenecity (many internal echoes), peculiarly when occurring in combination, may carry a college chance of an underlying malignancy.
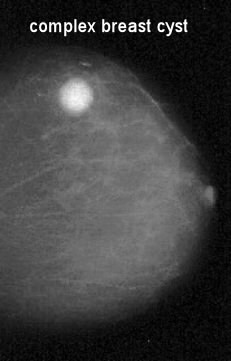
Higher up is a flick of a complex cyst on a mammogram. To the radiologist, it could exist anything, solid or a liquid cyst, and so it would need an ultrasound.
Charge per unit or hazard of malignancy associated with complex breast cysts
The vast majority of complex breast cysts turn out to be benign. As for those that eventually show as developing due to cancerous chest cancer, there is quite a range of stance as to the 'malignancy rate'.
This is probably due to the fact that in that location is no consequent definition of a complex cyst. Some studies place the rate as high as 63%, others as depression as 0.iii %. So, the best reply is, 'what does the histological evaluation say".
The ultrasound confirmation of a complex cyst of the breast can not be generalized as having any particular or consistent rate of association with breast cancer.
Of involvement, a personal or family history of breast cancer, and menopausal status appear to have no bearing on the development of a cancerous neoplasm.
Biochemically distinct types of breast cysts?
One of the trends in cancer research is to wait for unlike biochemical
Dissimilar cells may release different proteins and other chemicals, and that can give clues every bit to diverse jail cell growths and patterns that may be developing.
With breast cysts, there does appear to exist a tendency towards two basic 'lining patterns'. Firstly, those lined with apocrine epithelium and secondly, those lined with apartment epithelium. (Apocrine epithelial cells are basically secretion cells, while 'flat epithelium' refers to a flat or columnar 'stacking pattern' or layering of normal epithelial cells.)
The different cyst-lining cell patterns can too be measured biochemically using [Na+]/[K+], ( the 'sodium to potassium ratio' ) of the cystic fluid. In that location is some proposition that cysts with 'low electrolyte' readings ( higher potassium and less sodium) may indicate a higher risk for breast cancer involvement, simply this is purely speculative at this fourth dimension.
If the 'wall' of a complex cystic breast mass is getting thicker, there may be additional issues.
In summary, this 'biochemical-analysis' approach for evaluating breast cysts suggests that where the epithelial wall is 'getting thicker' past calculation certain types of cells, the risk of malignant association may be higher.
The lobulated cyst
The word
I don't personally use the word lobulated for cysts. This is because it causes people to search for the meaning of the word and become broken-hearted for no good reason.
A lobulated cyst, refers just to the surface of it and is just a cyst. On the other manus, a lobulated solid nodule has a different significance birthday.
A solid nodule that bulges in a fashion that is not a perfect sphere, tin betoken that some internal parts of the nodule are growing faster than other parts, which is a balmy inkling the solid nodule might be cancer.
But since a cyst has nothing growing inside it, the lobulated cyst surface is caused from outside of the cyst. Probably, the cyst is simply lying confronting a gristly band or blood vessel that doesn't stretch as easily as everything else around the cyst. So, I hope y'all relax nearly the lobulated cyst.
Shall we Q and A together?
What is complicated about a complex cyst of the breast?
Nobody knows how cysts can become blood or grunge in them, or fibrin balls that look like internal nodules. And so, this is why they are classed as 'complicated'.
Should information technology exist removed?
What is the treatment of a complicated breast cyst? In
What are the symptoms of a circuitous cyst and why?
A complex cyst of the breast can hurt because it has expanded into surrounding tissue. And so, the surrounding tissue says, 'who invited you, quit crowding me, yous're so pushy'. Next, the nervus endings for hurting sensation start sending signals of pain to your brain.
What percentage of circuitous cysts are cancerous?
Not exactly Goose egg, but very close in fact, according to medical studies around 0.iv%.
Where practise circuitous cysts grow and form?
Anywhere in the fibro-glandular cone of chest tissue, but not in the pure fat. Short-answer, near anywhere.
What color is breast cyst fluid?
Normally articulate yellow, or resembling tea color or beer color. The color might have a slight tinge of reddish. A complex cyst may have some extra colors, such every bit a little cloudy grayness or green in the fluid. If you looked at the fluid in a glass vial, you lot might see speckled debris floating.
When to aspirate or remove the cyst?
If the radiologist recommends it, go ahead and aspirate. Or, if the cyst hurts you, You lot tin ask for information technology to be drained or removed. Aspiration is easier.
Why do cysts grow? Tin can cysts burst or rupture?
Cysts do not normally burst or rupture unless someone punches actually hard at them. They abound to the size where surrounding pressure stops them and then they finish growing.
Farther Reading
- What is a Chest Cyst
- Clusters of Breast Microcysts
- Index of ALL our Benign Breast Conditions
- Fibrocystic Breast Disease
- Epidermoid Breast Cyst
Render to Homepage
References
- Houssami N, Irwig Fifty, Ung O. (2005) Review of complex breast cysts: implications for cancer detection and clinical practice. ANZJ Surg 2005;75:1080-1085. https://world wide web.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16398815
- Lindfors KK, O'Connor J, Acredolo CR, Liston CE. (1998) Brusk-interval follow-upward mammography versus firsthand core biopsy of benign breast lesions: cess of patient stress. AJR 1998;17l:55-58 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9648763
- Mannello F, Gazzanelli G. (2001) Prostate-specific antigen (PSA/hK3): a further player in the field of breast cancer diagnostics? Chest Cancer Research 2001, 3: 238-243. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC138688/
- Omori LM, Hisa North, Ohkuma Thou. (et al). (1993)Breast masses with mixed cystic-solid
sonographic appearance. J Clin Ultrasound 1993;21:489-495 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8270665 - Tea MM, Grimm C, Bikas D, Kroiss R, Fink-retter A, Kubista E, Wagner TM. (2007) The validity of complex breast cysts after surgery. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 2007 ASCO Annual Coming together Proceedings Part I. Vol 25, No. 18S (June 20 Supplement), 2007: 1519 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18649871
- Venta LA, Kim JP, Pelloski CE. (et al). (1999)Management of complex chest cysts. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1999;173:1331-1336. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10541113
mcdonoughandeverien.blogspot.com
Source: https://breast-cancer.ca/comp-cysty/
0 Response to "what are the chances that the biopsy onmy right breast can be nothing due to menstuation"
إرسال تعليق